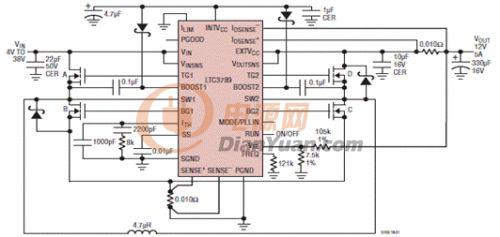
我采用LTC3789设计了一个输入4~24V,输出5V 6A的电路。但是在测试的时候出现了下面的问题。
我设计时,开关频率设计为600KHz
1、输出纹波过大,并且有一定的尖峰,尖峰频率在150KHz左右,空载时的纹波就已经在100mV了。4A负载时,纹波峰峰值达到了300~400mV。基本上是由于尖峰产生的。
2、仔细检测了尖峰产生的原因。测试条件如下:输入电压12V,输出电压5V,空载。
用示波器检测A、B桥(输入侧)驱动引脚波形正常,属于PWM控制信号。但是C、D桥(输出侧)波形异常。按照datasheet的说明,在降压情况下,应该只有A、B桥工作,C桥应该是常开,D桥应该是常关。相应地就要求C桥的控制信号为高电平,D桥的控制信号为低电平。但是在实现测试时发现C桥为高电平,但是每四个时钟周期就有一个低电平脉冲,D桥为低电平,但是每四个周期就有一个高电平脉冲,导致输出端就有相应地电压尖峰出现,并且转换效率也很低。空载时的输入电流达到了33mA。